What is lung function test / Pulmonary function test / spirometry?
PFT is a simple breathing test to assess your lung capacity
It is ordered by a chest/lung specialist if you are suspected to have obstruction/restriction in your lungs and also differentiate between breathlessness due to lung or heart conditions
This simple test helps in grading the severity and assists in monitoring the improvement/deterioration of the lung disease
When should you undergo this test?
Visit lung/chest specialist if you have complaints of
- Breathlessness which is increasing in severity
- If you have ever smoked cigarettes/bidis/hukkahs etc
- If you have persistent cough
- If you are exposed to fumes in a factory
- If your chest produces whistling sound especially with changes in weather
What is your role in spirometry / PFT?
Patient plays the most important role in spirometry. The procedure is divided into four stages
Stage 1:
Patient is instructed to take a deep breath in order to completely fill his lungs with air
Stage 2:
Patient is instructed to blast the inhaled air out like blowing 100 candles at one time
Stage 3:
Patient is instructed to blast the inhaled air out like blowing 100 candles at one time
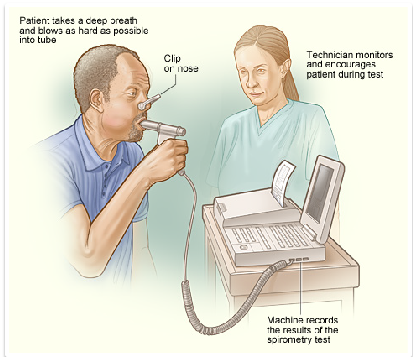
Stage 4:
Here, patient is instructed to take a deep breath
- The machine records the patient’s speed and the amount of the air that he/she blows into the device
- The report is generated as per the patient’s performance
- You may also be administered a inhaler in order to see your response to the medicine and lay a good probability of your diagnosis
What does the report signify?
The report quantifies the speed of the air blown/amount of the air blown in the form of numbers and graphs
The physician carefully analysis your report
He is now able to confirm his diagnosis of airway disease after interpreting the report
Sample PFT report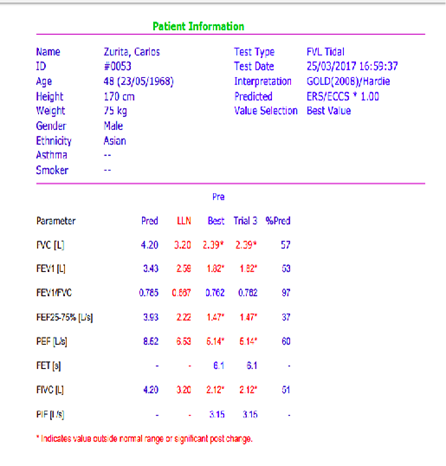
Important parameters in the report
- FVC(forced vital capacity)
- FEV1(forced expiratory volume in 1sec)
- FEV1/FVC
- FEF 25-75%(forced expiratory volume from small air sacs)
